Defending against an invisible enemy
Can laws solve the problems of noise pollution?
How can local representatives protect people from an invisible, ever-present hazard? That’s the question small governments across Nassau County have been trying to answer when it comes to noise pollution — all to varying degrees of success.
“Inevitably, you might be creating a standard that is unfair, that is inequitable,” said Kevin Walsh, an attorney who’s helped draft noise ordinances for municipalities like Malverne and Farmingdale. “Not because it isn’t applied equally, but because it hurts people that don’t have a problem with it.”
Noise pollution — excessive or frequent noise — is said to come with health risks like increased stress, hypertension and sleep disruption, according to the World Health Organization. But for some communities, dealing with excessive noise is nothing new.
Glen Cove’s noise ordinance, for example, has been largely unchanged since 1997, limiting noise that is “clearly audible at 50 feet.” Village ordinances for Sea Cliff — dating back to 1995 with updates more than a decade ago — define unreasonable noise as any constant, continuous or repetitive loud sound which “annoys” or “disturbs” the peace and comfort of neighboring residents.
But — despite what neighbors of barking dogs or chronic partiers may wish — there is no legal definition of “annoying.” Noise ordinances often use subjective language, because noise pollution is a subjective experience, Walsh said. Sound that irks one neighbor may be hardly noticeable by another.
Finding a way to differentiate
“It’s difficult because it’s trying to regulate human behavior,” he said. “When you try to regulate people’s enjoyment of their existence like this, on relatively subjective degrees, it’s a problem.”
When someone wants to play music while their neighbor wants their child to go to sleep, where does law enforcement draw the line? The incongruous — yet equally defensible — interests are “making it more and more difficult to get a balance between what is acceptable noise and what is not,” Walsh said.
“It’s a no-win situation, because, inevitably, you make one person happy. You’re making one person sad.”
Managing these conflicting expectations can result in local officials walking a tightrope. But Elena Villafane, Sea Cliff’s mayor, says that is an inherent part of serving the community.
“So, as with every local government, where you are managing how people reside in a community together, you're always balancing a variety of interests.” she said. “Right now, we seem to be at a happy equilibrium.”
Finding that balance
So, the question becomes, what is a fair standard to regulate noise? Do municipalities put the noise limit at the lower end to shield more sensitive people, and risk discouraging others from enjoying time outside? Or do municipalities create more lenient ordinances that allow more noise, and risk leaving sensitive people unprotected?
It’s a balancing act Glen Cove has had to grapple with.
“It is a very subjective criteria when one person's noise pollution is another person’s ‘fun time,’ so to speak,” said Christopher Ortiz, deputy chief of the Glen Cove Police Department. “So, in that sense, it is difficult trying to precisely determine what is an excessive amount of noise, and it becomes kind of a gray area.”
And that “fun time” is on the rise, especially since Covid-19. People these days are spending more time in their backyards since the pandemic, Walsh said.
Malverne mayor Tim Sullivan noticed that trend as well.
“What we found is, during Covid, a lot of homeowners invested in their backyards,” Sullivan said. “Whether pools, or outdoor bars and kitchens and sound systems. The backyard has become a renewed entertainment focus of the home.”
Sound-measuring technology, though, has dramatically improved in the decades since those original laws were passed, Walsh said — another reason why more governments across the county are passing updated noise ordinances.
Malverne’s noise ordinance, passed in December, limits outdoor music to 80 decibels — about the noise level of a vacuum cleaner — measured at the property line. Glen Cove considers 65 decibels — about the noise level of a conversation — “disturbing,” but also allows for subjectivity by employing a standard of whether the noise is “clearly audible” at 50 feet.
Too many variables?
But even something seemingly objective — such as a measurable standard like decibel level — presents new obstacles. A noise level that constitutes a nuisance to one neighbor may not bother another.
Sometimes, Walsh said, police will visit a property that is technically violating the noise ordinance, but the officer will personally find that the sound level or quality shouldn't break the law. So even with a measurable standard, enforcement is subjective.
And the actual sound level isn’t the only thing that matters — the source does, too.
Things like fire whistles and barking dogs polarize neighbors, Villafane said. Gas-powered leaf blowers are another malefactor that often earn their own section of noise ordinances.
The city ordinances also differentiate between how much noise various types of properties can make at different times. For example, a private residence can be penalized for making 50 decibels or more of noise after 10 p.m., and before 7 a.m., while a commercial property operating at the same time would need to reach 70 decibels before neighbors can make a complaint.
These different standards for businesses and private residences can sometimes boil over in communities. Because Long Island is very much suburbia, Walsh said, the interests of commercial and residential parts of towns often conflict — commercial districts often create more noise, which is at odds with the interests of residential communities that typically neighbor them.
Fly-by-night (and day) noise
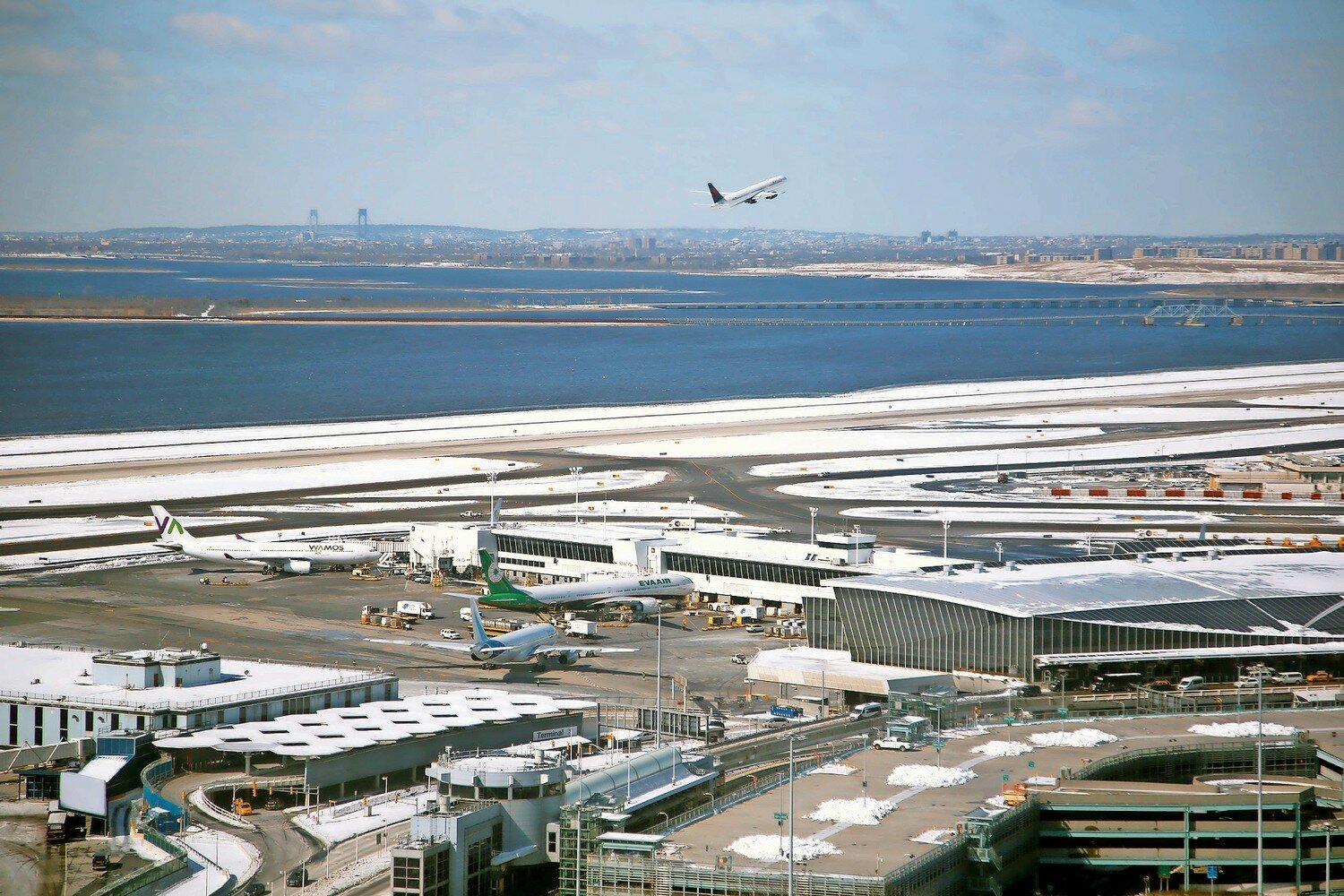
But the arguably biggest culprits of excessive noise may also be the hardest to manage. The constant drone of airplanes flying overhead is seemingly ever-present, but comes with its own challenges.
With John F. Kennedy and LaGuardia airports right next door, neighbors across the county are dealing with the near-constant drone of planes flying overhead.
The Town of Hempstead created the Town-Village Aircraft Safety and Noise Abatement Committee to deal specifically with this nuisance. But try as they might, local government has no sway over the conduct of airplanes — that’s all the Federal Aviation Administration.
“Everyone wants airlines to be safe,” said James Vilardi, the noise abatment committee’s executive director. “But is there a way to maintain the highest levels of airplane safety, and to accommodate the residents on the ground that are dealing with the airplane influence? We maintain that there is.”
The committee’s primary goal right now is to get accurate, specific decibel readings from FAA monitors. The problem, Vilardi said, is the information the FAA provides right now is warped because the decibel readings are averaged out among neighborhoods.
But if the committee gets the raw data and finds that the decibels violate municipal or federal code, they can appeal to the FAA to make changes.
The FAA, however, is largely unwilling to even acknowledge the noise abatement committee.
“It’s difficult to make changes in their policy without them being willing to talk to us,” Vilardi said. “We're pushing as hard as we can to get this data so we can have a real conversation with them.
“Unfortunately, it's a problem that our residents face, that our local elected officials do not have the power to directly impact. “There’s no way that the supervisor — or the county executive, or even a congressman — can say ‘OK, stop flying over Franklin Square.’ Or ‘fly 20 feet higher.’
“They just don't have the jurisdiction to do it.”
The timeline for progress is in the air, so to speak, until the federal agency finally has a dialogue with the town.
In the meantime, local governments are still striving for progress in the fight against noise pollution using new and updated noise ordinances. Although noise is largely inescapable, its excess can be mitigated when we focus on what we can control, experts say — local government’s responsibility to us, and our responsibility to each other.

 44.0°,
Mostly Cloudy
44.0°,
Mostly Cloudy